Get Started
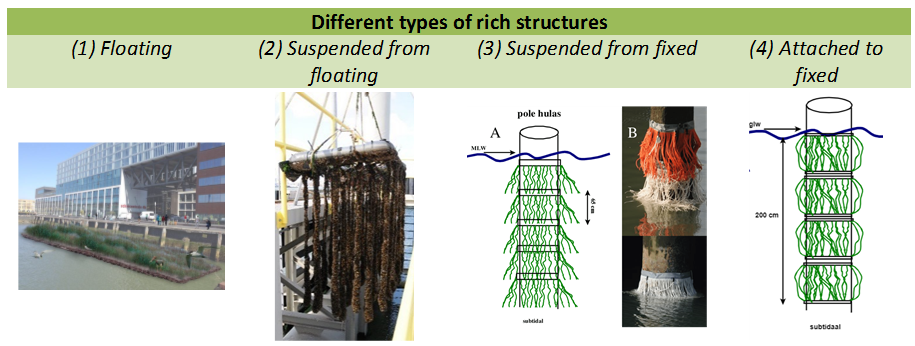
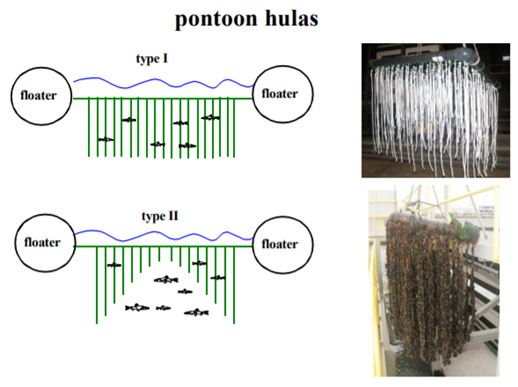
Hanging and floating structures are small-scale structures that provide habitat for organisms, can make a landscape more attractive and can be used to dampen wave energy which can contribute to lower maintenance costs of quay walls. There are different types of hanging and floating structures (see image below). Examples are floating marshes (type 1), pontoon hulas (type 2) en pile hulas (type 3/4). The structures are relatively easy to apply and offer opportunities for added services even when physical conditions or design constraints require hard solutions and/or provide little space for Building with Nature.
Advantages compared with a ‘traditional solution’
Advantages of hanging and floating compared to ‘traditional solutions’ include:
- Ecosystems and physical conditions:
- Provision of ecologically valuable habitats for organisms. Floating marshes are appealing to birds and insects, fish can find shelter beneath them. Pile/pontoon hulas provide valuable substrate for many species including mussels. Furthermore, they serve as a source of food for fish and as breeding grounds.
- Decreased hydraulic loads on the foreshore / embankments. Floating structures can reduce hydraulic loads caused by currents and waves.
- Reduced turbidity. More substrate for filter feeders increases the amount of filtering of the water, resulting in reduced turbidity.
- Socio-economic:
- Contribution to an attractive landscape for recreation. Floating marshes increase spatial quality and provide opportunities for recreational fishing.
- Potential for collection of edible (shell)fish and plants.
- Hanging and floating structures may extent lifetimes of structures (e.g. shellfish frames against quay walls may slow down corrosion).
- Governance:
- Construction of a rich structure can contribute to meet the requirements of environmental legislation such as water framework directive and Natura 2000.
- Floating marshes can be used as climate mitigation measure as they can capture CO2.
Disadvantages compared with a ‘traditional solution’
Disadvantages of hanging and floating structures compared to ‘traditional solutions’ include:
- Construction of a hanging or floating structure could add to the costs of the project in case application does not reduce other costs (e.g. reduction maintenance costs of quay walls);
- Added attractiveness for recreation could add additional safety risk for the public or hinderance to the surrounding;
- Hanging and floating structures could provide habitat for invasive species.
- The structures require maintenance.